Understanding the Function and Applications of Blind Motors
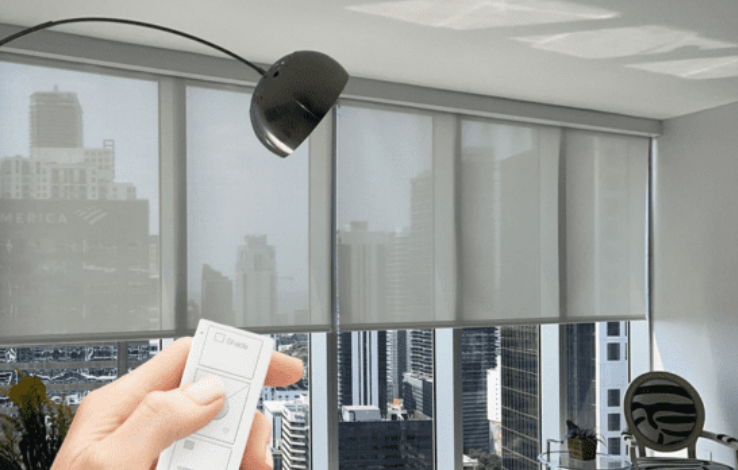

Introduction to Blind Motors
Automation has revolutionized the way we manage both residential and commercial environments. One of the key components enabling this shift is blind motors. These motors are designed specifically to operate window coverings such as roller blinds, shutters, and curtains. For industries like PCBA manufacturing, blind motors are particularly interesting because they combine mechanical functionality with electronic control, requiring precise circuit assembly to ensure reliability and efficiency.
How Blind Motors Work
Blind motors operate using an electric motor mechanism connected to a control system. When powered, the motor rotates a shaft or drum to raise, lower, or tilt the blinds. The integration of control electronics allows for smooth acceleration, deceleration, and precise positioning. Many modern blind motors also include feedback systems that monitor movement and stop the motor at set limits to prevent over-rotation or mechanical strain.
Key Features of Modern Blind Motors
Blind motors are designed to meet the needs of contemporary users, offering several advantages over traditional manual systems:
Quiet Operation
Noise reduction is essential, particularly in homes and offices. Blind motors are engineered with low-noise gears and vibration-dampening components, providing near-silent operation.
Energy Efficiency
Blind motors consume minimal power, which makes them suitable for long-term operation. Efficient design not only reduces energy costs but blind motors also limits heat generation, extending the motor’s lifespan.
Compact Design
The compact form factor allows blind motors to fit inside narrow housings while maintaining high torque and performance. This design ensures compatibility with various blind and shutter types.
Smart Functionality
Many blind motors are compatible with timers, remote controls, and smart home systems. Users can schedule opening and closing, integrate with light sensors, or control motors remotely via mobile applications.
Applications in Residential Environments
In homes, blind motors are often used to automate window treatments, offering convenience and energy savings. Automated blinds help control sunlight, reduce glare, and improve privacy. They are particularly valuable in rooms with multiple windows, large panoramic windows, or hard-to-reach areas where manual operation is inconvenient.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency
By controlling sunlight and heat, blind motors can help reduce cooling and heating loads, contributing to energy efficiency and lower utility bills.
Improving Home Comfort
Automated blinds provide consistent control over indoor lighting and temperature, enhancing comfort in living spaces and work areas.
See also: How Is Smart Technology Changing Excavator Operations?
Applications in Commercial Settings
In commercial buildings, blind motors offer additional benefits. They allow synchronized operation across multiple windows, improving visual comfort and reducing glare on computer screens. Offices, meeting rooms, and public spaces can benefit from motorized window systems that adjust automatically based on time of day or ambient light levels.
Corporate Energy Management
Blind motors can be integrated into building management systems to optimize lighting and climate control, supporting sustainability initiatives and energy-saving policies.
Safety and Accessibility
Motorized blinds reduce the need for manual handling, enhancing safety for staff and visitors while making window management accessible to all individuals.
Integration with PCBA Manufacturing
Blind motors rely on precise electronic components for accurate operation. In PCBA manufacturing, the motor controller is a key part of the system. It includes microcontrollers, sensors, and driver circuits assembled on a PCB to regulate motor speed, direction, and position. Proper PCB assembly is critical for reliability, as faults in the electronics can lead to malfunction or motor damage.
Importance of Accurate Assembly
Manufacturers must ensure that components are correctly placed, soldered, and tested. Automated optical inspection and functional testing are commonly used in PCBA manufacturing to maintain high-quality standards for motor control boards.
Role of Sensors
Some blind motors use Hall sensors, encoders, or limit switches to provide feedback to the control board. Accurate sensor integration ensures smooth and precise movement of blinds.
Selection Criteria for Blind Motors
Choosing the right motor involves several considerations:
Torque and Power Requirements
The weight and size of the blinds determine the torque needed. Motors must be capable of handling the load while maintaining smooth operation.
Voltage and Compatibility
Blind motors come in various voltages, including low-voltage DC and standard AC options. Compatibility with the control system and power supply is essential for safe and reliable operation.
Control Options
Depending on user preferences, blind motors may support wired controls, remote controllers, or smart home integration. Selecting motors that fit the intended control method ensures a seamless user experience.
Environmental Suitability
For outdoor or high-humidity areas, motors with protective coatings or suitable IP ratings prevent damage from moisture and dust, extending the motor’s lifespan.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Correct installation and regular maintenance are vital for ensuring the optimal performance of blind motors.
Installation Guidelines
Motors should be installed according to manufacturer instructions, with attention to alignment and mounting stability. Proper installation prevents uneven movement, noise, and mechanical wear.
Maintenance Tips
Routine inspections include checking for debris, ensuring proper lubrication, and verifying the integrity of electronic connections. These steps help prevent malfunctions and prolong motor life.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Typical issues include power interruptions, mechanical obstruction, or PCB faults. Knowledge of both electronic and mechanical aspects allows technicians to resolve problems efficiently.
Benefits of Blind Motors
Incorporating blind motors offers multiple advantages:
- Convenience: Eliminates manual operation, particularly for large or hard-to-reach windows.
- Energy Efficiency: Optimizes natural light and reduces heating or cooling demands.
- Safety and Accessibility: Provides safe operation and enhances accessibility for all users.
- Smart Integration: Enables automation and remote control for modern living and working spaces.
Future Developments in Blind Motor Technology
The technology behind blind motors continues to advance. Trends include:
- IoT Integration: Motors integrated with smart home systems allow remote control, voice commands, and automated schedules.
- Improved Sensors: Enhanced sensor technology increases positioning accuracy and motor responsiveness.
- Energy Harvesting: Some designs incorporate solar power or low-energy consumption methods for sustainable operation.
Conclusion
Blind motors are an essential component in modern automated environments, providing convenience, energy efficiency, and precise control for both residential and commercial applications. For industries like PCBA manufacturing, these motors highlight the importance of quality PCB assembly and integration with electronic control systems. Selecting the right motor, ensuring proper installation, and performing regular maintenance are crucial steps in achieving reliable performance. As automation technologies continue to evolve, blind motors will remain a key feature in smart homes and intelligent building solutions.